Making a user administrator is usually the best way to give a user access to sudo, but this guide will show you how to modify Sudoers file to give a user or group access to sudo. If you are changing a user's group(s), follow our guide on safely changing user's primary group. Giving the user or group access to sudo will allow them to update the OS with ‘apt-get’. 'Apt-get' does not allow for updates through versions such as Ubuntu 12.04 to Ubuntu 14.10. If you are doing that, back up your files and follow our guide on installing Ubuntu Server.
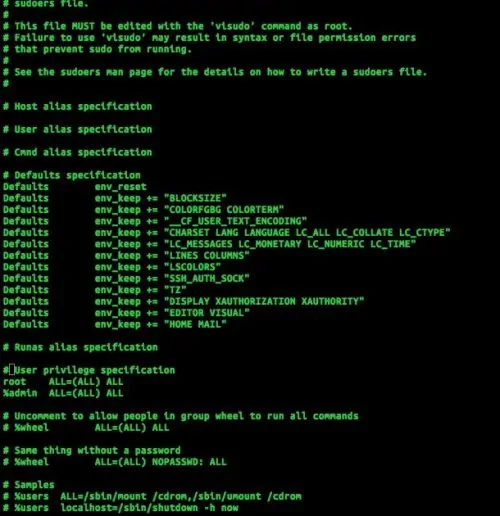
To modify sudoers file, the command visudo should be used because it reads the sudoers file for errors before saving it. However, ‘nano’, and ‘vi’ can be used (But they must be ran as root). I will be using visudo for this guide because it has protections built-in that (at least) make it harder for you to incorrectly edit Sudoers. Be careful about using spaces and tabs when starting to modify Sudoers file because incorrect spacing can damage the file and cause the OS to fail to boot properly. [Read: Force Ubuntu boot into terminal by default]
To begin, close all applications and run:
<br /> sudo visudo<br />
It will then request you for your password (which you should type in). After you type in the password, you should be ready to edit sudoers file.
Table of Contents
Examination before beginning to Modify Sudoers
Depending on the Linux distro you are using, this may open up in 'vi', 'nano', or another text editor. There is no difference between the text editors for ‘visudo’ other than preexisting differences between them. 'Visudo' on the Ubuntu-Core will open up 'nano' by default. The comments on the top are warnings to only use ‘visudo’ for editing it and to read the sudoers man page. I recommend you read the man page for visudo by running man Visudo. Now you will see some comments with nothing underneath them other than another comment. This guide will not be going over those comments and what goes beneath them. [Read: How to create shortcut / aliases to commands in Ubuntu using .bash_aliases?]
Modify User Privileges
Now find the following comment:
<br /> # User privilege specification<br />
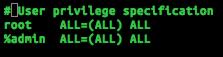
Under that is:
<br /> root ALL=(ALL) ALL<br />
Note the space between 'root' and 'ALL=' is a tab and between '(ALL)' and 'ALL' is a space. It is worth noting here that the tab will not necessarily appear to be the full length of a tab. This specification gives the user ‘root’ permission to run all commands in sudo with a password. To add a user to sudoers list, modify sudoers file and simply retype the above line but put the user you want to have permission to run all commands in sudo in the place of ‘root'. Pay attention to the spacing.
<br /> test ALL=(ALL) ALL<br />
Edit Groups Privileges
Now the user ‘test’ will have permissions to run any command as root. But now you need to give the group ‘alpha’, permission to use sudo for all commands, so just add a ‘%’ in front of the ‘alpha' to signify that it is a group and put it below ‘# User privilege specification’. Again, just replace ‘alpha’ with the group you want to use.
<br /> %alpha ALL=(ALL) ALL<br />
Recommended Guides:
No Password for Sudoers
Now group ‘alpha’ can run commands as root. Every session you have to type in your password to use sudo once, which can be very inconvenient. To make an account have Sudoers Nopasswd permissions, add a ‘NOPASSWD:’ after the second ‘(ALL)’ and a space. If you are doing this for the group ‘admin’, simply modify the preexisting line:
<br /> %admin ALL=(ALL) ALL<br />
to:
<br /> %admin ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL<br />
When you are done modifying the sudoers file, (use the text editors exit function like ':w' then ':q' for 'vi') and reboot. Remember to pay attention to spacing. While disabling passwords during testing can be hugely conveniently, please realize that it creates a huge security risk. Therefore, we do not recommend disabling password for sudoers. [Read: How to install Webmin on Ubuntu and secure it?]
Summary
That is all there is to editing sudoers file in Ubuntu and other Linux distros. If you are setting up a VPS (we r or your own home server, this knowledge can come in handy. [Read: Digital Ocean vs Synthesis – 10 reasons why I chose Digital Ocean VPS]
So go ahead modify sudoers file and give a specific user or group admin privileges and start administering your server the right way.



![Ultimate QNAP Docker Compose and Container Station Guide [2023] QNAP Container Station](https://www.smarthomebeginner.com/images/2023/05/ContainerStation.png)
![Ultimate Docker Server: Getting Started with OS Preparation [Part 1] Docker Server Tutorials 1 OS Preparation](https://www.smarthomebeginner.com/images/2024/01/Docker-Series-01-Intro-and-OS-Prep.png)
