What is Permalinks?
WordPress defines permalinks as "Permalinks are the permanent URLs to your individual weblog posts, as well as categories and other lists of weblog postings. A permalink is what another weblogger will use to link to your article (or section), or how you might send a link to your story in an e-mail message. The URL to each post should be permanent, and never change — hence permalink.".
Why change Permalinks?
If you read around you will find that changing the permalink structure will help with search engine optimization. By default WordPress's URL structure looks like this:
http://domain.com/?p=1150
As you can it conveys nothing about what the page is about. By having a short post title in the URL it not only optimizes the page for search engines but also it gives the visitor an idea of what the page is about from within the search results. In many cases this might be a reason for the visitor to pick your post among all the search results.
What Permalink Structure is the Best?
WordPress offers several permalink structures. Having category names is can be tricky if you have each post assigned to multiple categories. Having dates can be detrimental to older posts. Therefore, my recommendation is to go with the following:
Postname: http://domain.com/sample-post
How do I change Permalink Structure?
This procedure assumes the following:
- You are running WordPress (>=3.0) on a Linux server
- You are running Apache with virtual hosts defined in /etc/apache2
- You currently have the default permalink structure
For other scenarios, check this page.
First, enable Apache's rewrite module using the following command:
sudo a2enmod rewrite
If it is already enabled, you will see "Module rewrite already enabled".
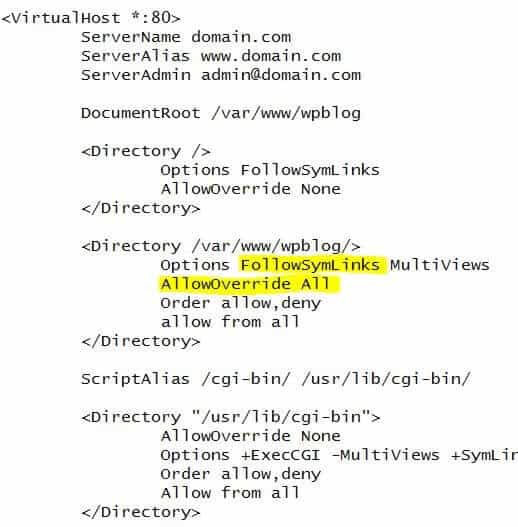
Next, edit your virtualhost file to enable FollowSymLinks option and FileInfo directives:
cd /etc/apache2/sites-available sudo nano domain.com
Note that "domain.com" is the name of your WordPress site. Then edit the file as shown below (highlighted sections):
Then, go to your WordPress root directory. If there is not .htaccess file create one and change its permissions to 775:
touch .htaccess sudo chmod 775 .htaccess
Restart your Apache server:
sudo service apache2 restart
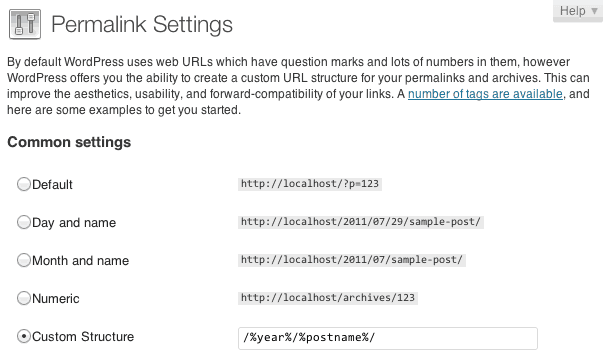
Next, go open your WordPress Dashboard and go to "Permalinks" under "Settings". Choose the permalink structure that says:
Post name: http://domain.com/sample-post/
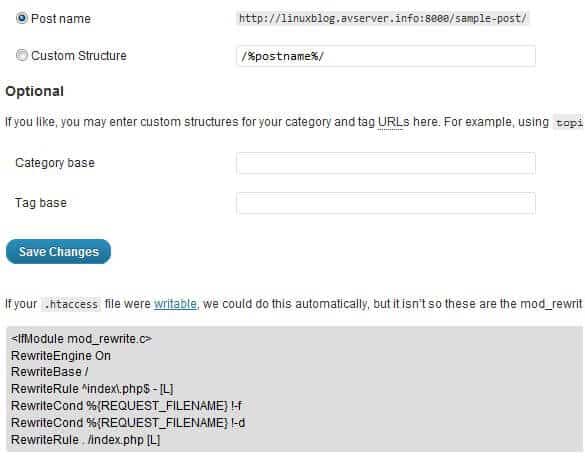
At the bottom of the screen you should see the appropriate redirect code to be added to the .htaccess file in WordPress root directory. If you created a .htaccess file as described above and changed its permissions to 775 then all you have to do is to click "Save Changes" and the redirect rules will be automatically added to your .htaccess file. If you already have a .htaccess file, WordPress will append to it and not remove any of the existing content.
Then move to your WordPress home directory and change the permissions of .htaccess file to 644 for security reasons:
sudo chmod 644 .htaccess
Alternatively, if you prefer not to play with permissions you can manually open the .htaccess file in a text editor and copy past the redirect rules that you see at the bottom of the screen. If you are changing from default "?p=1150" to "Post name" permalink structure then your rewrite rule will be:
<ifmodule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index.php$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.php [L]
</ifmodule>
The redirect rules .htaccess file will ensure that all your old posts that were created with "?=1150" permalink structure will automatically redirect to the new structure.
Finally, restart your Apache once more and you are done.
sudo service apache2 restart
Your WordPress blog should now have a readable URL and be more search engine and visitor friendly.
If you would like to enable SSH2 support for your WordPress blog for easy maintenance and updates, please read this post.
Happy Blogging!

![Ultimate QNAP Docker Compose and Container Station Guide [2023] QNAP Container Station](https://www.smarthomebeginner.com/images/2023/05/ContainerStation.png)