Before you go out to shop for a smart home product, you discover in your research that some smart lights aren’t compatible with some smart switches, and the same goes for smart home cameras and other products. That’s because the protocol these devices are using is different.
There are several smart home protocols available, each with its own pros and cons, strengths, and weaknesses, and device manufacturers carefully select the one that’s best for their product.
But this leaves the end user — you in confusion and agony.
However, we decided to simplify this for you by explaining each protocol's strengths and weaknesses, so moving on, you can buy products with your favorite protocols that also meet your requirements.
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Smart Home Protocols Explained
Let me introduce you to the smart home protocols first before I talk about them in a bit more detail.
- Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
- Z-Wave
- Zigbee
- Matter
- Thread
- X10
- MQTT
Now that you know what smart home protocols exist, let me briefly explain them to you!
1. Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is one of the most common IoT protocols. It’s hard to not be familiar with Wi-Fi unless you've been living under a rock.
Smart home devices that support Wi-Fi protocols can be set up in no time, plus they offer a huge bandwidth that makes them suitable for a wide range of IoT devices.

However, the same reason is what also makes Wi-Fi a tough sell since it's not ideal for battery-powered devices as the power consumption is higher. Plus, WiFis don’t cover a large area, the connection isn’t encrypted, and they are also susceptible to interference.
Also, most Wi-Fis offer a 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz spectrum, and there are several versions of the Wi-Fi standard, such as: 802.11b, 802.11a, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5), 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6).
Whichever Wi-Fi standard you use, be sure to set a strong Wi-Fi password that you will never forget.
2. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Bluetooth Low Energy is a lower-power-consuming variant of standard Bluetooth. It was developed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group and works on the 2.4 GHz spectrum and uses low power, making it one of the most common local connectivity protocols that is perfect for battery-powered smart home devices.
Plus, it offers low latency, has higher bandwidth, and can connect with a variety of IoT and wearable devices. However, it is severely affected because it has a very short range, and since it operates on the 2.4 GHz spectrum, it can suffer from interference.
On the flip side, Bluetooth uses AES-128 encryption and supports mesh networking as well.
3. Z-Wave
Z-Wave protocols operate on the low-frequency 908.42 MHz and offer data transmission speeds of 100 kbps. They are one of the most popular and widely used home automation protocols.
Because of the low frequency, there is no interference with Wi-Fi, and it can penetrate walls much more easily. However, the throughput and the data transmission speeds are lower, so smart home cameras and other smart devices that need higher bandwidth don’t use this protocol.
This protocol can be mostly found in smart home devices like thermostats, door locks, motion detectors, garage door sensors, switches, and other products, and since it uses mesh networking, all Z-Wave-compatible products also communicate with each other easily.
Additionally, if you didn’t know, Z-Wave and Samsung SmartThings collaborate flawlessly to communicate with smart devices.[Read: Best Smartthings compatible devices – Top 15 choices]
4. Zigbee
Another open-standard wireless mesh network is ZigBee. The technology was created with the specific requirements of Internet of Things (IoT) networks and low-power, affordable wireless smart home products in mind. [Read: 5 interesting and must-know facts: Z-Wave vs ZigBee]
It supports mesh networking, operates on the 2.4 GHz band, and is perfect for battery-based smart home devices. It supports data transmission speeds of up to 250 kbps and can communicate with up to 65,000 devices on a single network.
Several smart home products, like thermostats, lightbulbs, and more, use the Zigbee smart home protocol.
However, since it operates on the 2.4 GHz band, it is likely to face interference from your Wi-Fi at times, but compared to Z-Wave, this has higher data transmission speeds.
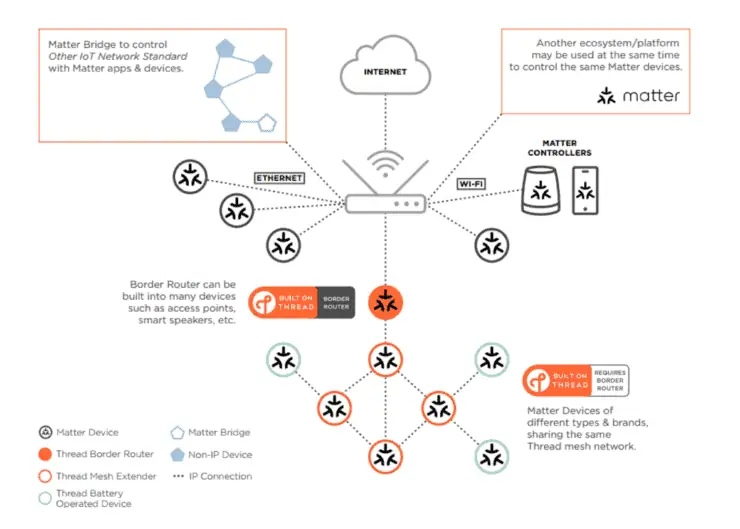
5. Matter
Matter is not a protocol but a new smart home standard developed by the Connectivity Standard Alliance, previously known as the Zigbee Alliance. Many smart home device manufacturers came together to create a standard that removes the restrictions and hindrances to seamless interoperability of smart home devices with different protocols.
This awesome matter protocol tutorial will get you up to speed on how this standard works.
Amazon, Apple, Google, Samsung, LG, Haier, Amazon, and Schneider Electric are some of the manufacturers who have committed to making products with the Matter standard, but this list is not exhaustive.
The architecture of Matter combines various components of existing home automation protocols to produce what may be a universal protocol.
6. Thread
The Thread Group, a group of rival businesses including Apple, Samsung, Google, Qualcomm, and others, manages and develops the Thread protocol.
Thread uses the IEEE 802.15.4 wireless standard on a 2.4 GHz band and can connect to over 250 devices securely using AES encryption.
Thread devices are based on IP networks, which means your smart home products can communicate with each other as well as communicate over the internet. It also uses the latest IPv6 instead of IPv4 to communicate with each other.
Using a Thread Border Router, you can also control your IoT devices that use the Thread protocol from anywhere in the world.
The thread protocol is also energy-efficient and has data transmission speeds of up to 250 Mbps.
7. X10
X10 is open-source as well as one of the oldest home automation protocols, developed by Pico Electronics of Glenrothes in 1975. It is very easy to deploy as it doesn’t require the installation of additional cables, and moreover, it is cheap.
Digital data is transmitted between X10 devices using your home's existing electrical wiring.
However, it takes 0.75 seconds between sending an address and a command. This can cause issues when two parties who are controlling shared smart devices send contradictory commands.
X10 smart home protocol is not as common as some of the others listed above, in a typical smart home environment.
8. MQTT
MQTT is an OASIS Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) for the Internet of Things (IoT). MQTT can scale to connect millions of IoT devices. While MQTT clients are small and use microcontrollers, MQTT can scale to support millions of IoT devices. MQTT is lightweight and fast, using small message headers to optimize network bandwidth.
MQTT today is used in many different industries, any that require support for IoT devices. These include automotive, manufacturing, telecommunications, smart enterprise, etc. Because many IoT devices connect over cellular networks that can prove to be unstable, MQTT supports persistent sessions to reconnect the client with the Mosquitto MQTT Broker.
Smart Home Devices with MQTT protocol are rare. Instead, intermediate MQTT gateways are normally used to connect a non-supported sensor to the home automation hub.
For example, a Home Assistant instance may not be able to connect to devices via Bluetooth (due absence of bluetooth controller). In this case, a Bluetooth to MQTT gateway connect to the bluetooth device, get the sensor data and send it via MQTT that Home Assistant can receive through a MQTT broker.
What protocol should you select as a newbie to smart home automation?
The answer to that depends on your specific needs and requirements. For instance, WiFi is one of the most common smart home protocols and is compatible with a wide range of devices and applications. However, the connection isn’t encrypted, it's susceptible to interference, and it doesn’t cover a large area.
Bluetooth Low Energy Protocol, on the other hand, is better than Wi-Fi on many fronts, but it has a short range.
Currently, Z-Wave and Zigbee are the best smart home protocols, and there are several IoT devices already on the market running these protocols.
But if you want to future-proof yourself, you should consider Thread and Matter smart home devices.
FAQ
What smart home protocol is best?
As the French say for everything, it depends - on your specific needs and requirements. Currently, Z-Wave and Zigbee are the best smart home protocols. But we believe Thread and Matter protocols is where the industry is trending.
What protocol is used for smart plug communication?
Smart plugs can communicate in many different IoT communication protocols, including Wi-Fi, Z-Wave, ZigBee, etc.
Conclusion
Now that you know what IoT protocols are available and which protocol to choose, we hope this article has answered your questions. All protocols have their own unique use cases, and if you’re still confused, reach out to your friends and family and ask them what smart home products they’re using with what protocol.
But remember that just because Thread and Matter protocols are here doesn’t mean IoT devices with Z-Wave or Zigbee are going to vanish anytime soon.
Or if you don’t want to deal with the hassle of going through different protocols and getting stuck in an ecosystem, run a smart home controller powered by Home Assistant, which has integration for over 1000 (and counting) services and devices.
Alternatively, if you do not mind changing batteries often, you can select Wi-Fi-supported IoT devices moving forward.



![8 Amazing Raspberry Pi Ideas [2022]: Beginners and Enthusiasts Raspberry Pi ideas](https://www.smarthomebeginner.com/images/2021/09/raspberry-pi-4-dev-board.jpg)


![10 Best Jellyfin Client Devices [2022] - 4k, Hardware Transcoding, etc. Jellyfin Roku App](https://www.smarthomebeginner.com/images/2021/02/jellyfin-roku-client-app-ft.jpg)
